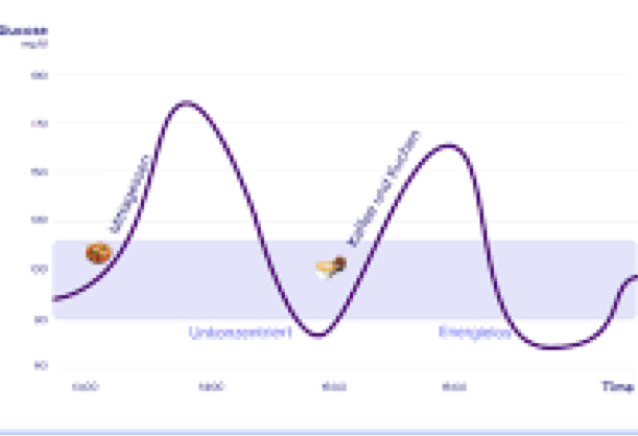
Why Should Blood Sugar Spikes Be Minimized?
Stable Blood Sugar Curve
Why should blood sugar spikes be minimized?
Blood sugar plays a crucial role in our daily lives as it provides the primary energy source for our bodies. However, how blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day can significantly impact our health and well-being. Particularly, large spikes in blood sugar that occur after consuming certain foods can be harmful in the long run. In this blog post, we will explore why it's important to maintain stable blood sugar levels and how to achieve this.
What Happens During a Blood Sugar Spike?
When we consume carbohydrates or sugary foods, the sugar from these foods is converted into glucose in the digestive tract and absorbed into the bloodstream. This leads to an increase in blood sugar levels, prompting the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps move glucose into cells, where it can be used for energy or stored as fat.
A blood sugar spike occurs when blood sugar levels rise rapidly after eating. This happens mainly when we consume foods with a high glycemic index—those that cause a quick rise in blood sugar. Examples include white bread, sugary drinks, sweets, and surprisingly, even some fruits.
Why Are Blood Sugar Spikes Problematic?
Energy Crash After a Spike
After a spike, blood sugar often drops quickly, leading to an energy deficit. This can manifest as fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Many people experience an "energy slump" after a sugary meal, which can drive them to reach for more sugary snacks, leading to a vicious cycle.Fat Storage and Weight Gain
High blood sugar spikes cause the pancreas to produce large amounts of insulin. Insulin helps transport sugar into cells, but if the body consumes more sugar than it needs, the excess is converted into fat and stored. Prolonged high insulin levels can lead to weight gain and obesity.Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Repeated blood sugar spikes can reduce the body’s sensitivity to insulin. This means cells become less responsive to insulin, and the body must produce even more to regulate blood sugar. This condition, known as insulin resistance, is a precursor to type 2 diabetes.Cardiovascular Disease
Insulin resistance and consistently high blood sugar levels increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. High blood sugar levels can lead to inflammation and damage blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
How Can Blood Sugar Spikes Be Prevented?
Incorporate Fiber into Meals
Fiber slows down the digestion of carbohydrates and the absorption of sugar into the blood. Consuming fiber-rich foods like salads, vegetables, and legumes can help slow and stabilize the rise in blood sugar.Combine Carbohydrates with Proteins and Fats
Proteins and healthy fats also slow sugar absorption. This means that a meal containing both carbohydrates, proteins, and fats leads to a more gradual increase in blood sugar. Good sources of protein include meat, fish, and plant-based alternatives like tofu, while healthy fats are found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil.Prefer Low-Glycemic Foods
Choose foods with a low glycemic index, which cause a slower rise in blood sugar. These include salads, vegetables, legumes, and certain fruits like berries. These foods provide a steady energy supply and prevent large blood sugar fluctuations.Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels by enabling cells to use glucose more effectively. Just 30 minutes of moderate exercise per day, such as walking or cycling, can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is vital for our health and well-being. Large fluctuations in blood sugar can lead to short-term energy issues and increase the long-term risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. A conscious diet rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, along with regular exercise, is key to keeping blood sugar levels stable and promoting a healthy life